The engine lathe is an accurate and versatile machine on which many operations can be performed. These operations are:
1. Plain Turning and Step Turning
2. Facing
3. Parting
4. Drilling
5. Reaming
6. Boring
7. Knurling
8. Grooving
9. Threading
10. Forming
11. Chamfering
12. Filing and Polishing
13. Taper Turning
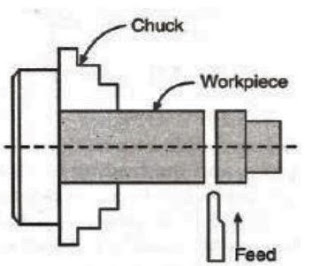
1. Plain Turning: Plain turning is the operation of removing excess amount of material from the surface of a cylindrical job.
2. Step Turning: Step turning produces various steps of different diameters.
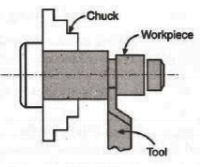
3. Facing: The facing is a machining operation by which the end surface of the workpiece is made flat by removing metal from it.
4. Parting: The parting or cutting off is the operation of cutting away a desired length of the workpiece, i.e., dividing the workpiece in two or more parts.
5. Drilling: Drilling is the operation of producing a cylindrical hole in the workpiece.
6. Reaming: The holes that are produced by drilling are rarely straight and cylindrical in form. The reaming operation finishes and sizes the hole already drilled into the workpiece.
7. Boring: The boring operation is the process of enlarging a hole already produced by drilling.
8. Knurling: The knurling is a process of embossing (impressing) a diamond-shaped or straight-line pattern into the surface of workpiece. Knurling is essentially a roughening of the surface and is done to provide a better gripping surface.
9. Grooving: Grooving is the act of making grooves of reduced diameter in the workpiece.
10. Threading: Threading is the act of cutting of the required form of threads on the internal or external cylindrical surfaces.
11. Forming: The forming is an operation that produces a convex, concave or any irregular profile on the workpiece.
13. Filing and Polishing: The filing is the finishing operation that removes burrs, sharp corners and feed marks from the workpiece. After filing, the surface quality is the workpiece is improved by the polishing operation with the help of emery cloth of fine grades.
14. Taper Turning: The taper turning is an operation of producing a conical surface by gradual reduction in the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece.