The planer is a machine tool
designed to produce plane and flat surface on a workpiece which is too large or
too heavy. The workpiece is securely fixed on a table called platen, and it
reciprocates horizontally against a single edged cutting tool. The surface
machined may be horizontal, vertical or at an angle.
Operations of planer machine:
The planer is used for:
- Planing
flat horizontal, vertical and curved surfaces.
- Planing
at an angle and machining dovetails.
- Planing
slots and grooves.
The planer are available in
different types for doing different types and sizes of job; the most common
being the standard and double housing planer.
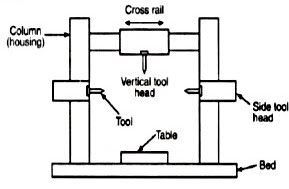
Construction
The main parts of the double
Housing Planer machine is Bed and table, Housings, Cross rail, Tool heads,
Driving and feed mechanism.
Bed
and table: The bed is a long heavy base and table made of cast iron.
Its top surface is flat and machine accurately. The flat top surface has slots
in which the workpiece can be securely clamped. The workpiece needs rigid
fixing so that it does not shift out of its position. The standard clamping
devices used on planer machine are: Heavy duty vice, T-holders and clamps,
angle plate, planer jack, step blocks and stop. The table movement may be
actuated by a variable speed drive through a rack and pinion arrangement, or a
hydraulic system.
Housings: The
housings are the rigid and upright column like castings. These are located near
the centre on each side of the base.
Cross
rail: The cross rail is a horizontal member supported on the
machined ways of the upright columns. Guide ways are provided on vertical face
of each column and that enables up and vertical movement of the cross rail. The
vertical movement of the cross rail allows to accommodate workpiece of
different heights. Since the cross rail is supported at both the ends, this
type of planer machine is rigid in construction.
Tool
heads: Generally two tool heads are mounted in the horizontal
cross rail and one on each of the vertical housing. Tool heads may be swiveled
so that angular cuts can be made. Driving and feed mechanism: The tool heads
may be fed either by hand or by power in crosswise or vertical direction. The
motor drive is usually at one side of the planer near the centre and drive
mechanism is located under the table. The size of the planer is specified by
the maximum length of the stroke, and also by the size of the largest
rectangular solid that can be machined on it.